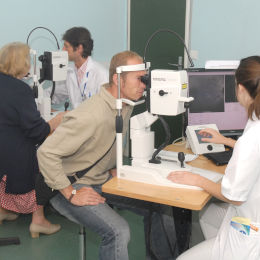
 Le service d’ophtalmologie de Créteil dispose d’un plateau technique comportant plusieurs moyens d’investigation clinique.
Le service d’ophtalmologie de Créteil dispose d’un plateau technique comportant plusieurs moyens d’investigation clinique.
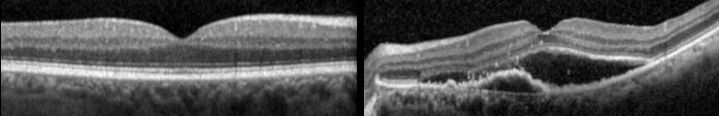
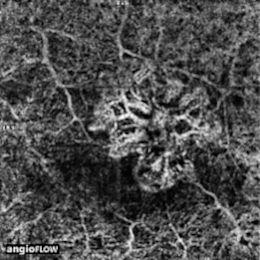
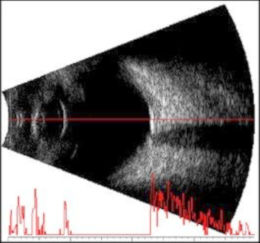
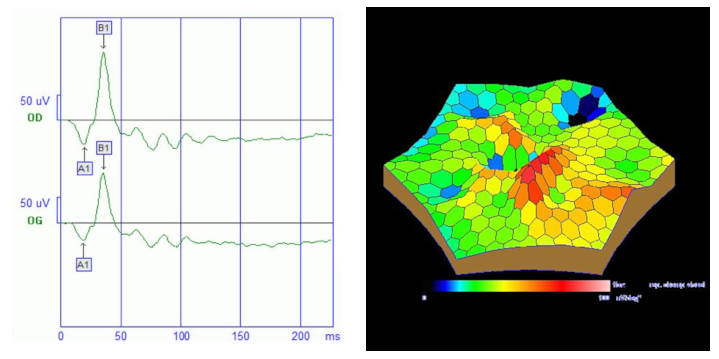
Ces techniques d’imagerie rétinienne et d'analyse fonctionnelle comprennent l'angiographie à la fluorescéine, l'angiographie au vert d'indocyanine, la tomographie en cohérence optique (OCT), l'OCT-angiographie, l'échographie oculaire, le champ visuel et l'électrophysiologie.
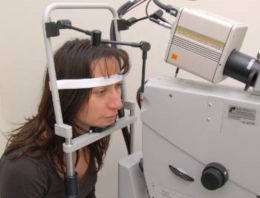
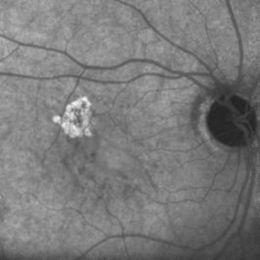
L’ angiographie à la fluorescéine est l'examen clé pour le diagnostic des maladies rétiniennes et plus particulièrement de la dégénérescence maculaire liée à l’âge.
La fluorescéine, qui est un colorant vital, est injectée dans une veine du pli du coude. Elle émet une lumière fluorescente lorsqu'elle est excitée par une lumière d’une certaine longueur d'onde. L'angiographie consiste à réaliser des photographies de la rétine lors du passage de la fluorescéine dans les vaisseaux rétiniens.